Do your dashboards inspire action? This article shares practical tips to help make them more actionable.
AndreyPopov | BigStock
Today, dashboards are everywhere. They’re omnipresent on our devices, computers and public displays. They help us manage the growing volume of data we’re tasked with processing on a daily basis. However, most dashboards still fail to provide what we want most—actionable insights. While most of us appreciate having more information at our fingertips, what we really need are insights we can act on. If dashboards can’t help us to optimize our performance, it’s questionable how much value they really offer us.
To illustrate the importance of actionable insights, I’ll share a real-world example from my sedan. My car’s dashboard has an indicator that appears when one of my tires has low air pressure. The engineers who designed the car decided I didn’t need to know which specific tire is low or by how much. Whenever the indicator goes off and I inspect the low-profile tires, it’s often difficult to pinpoint which specific tire is flat. In these scenarios, I receive an insight (“one of your four tires has low pressure”), but it isn’t sufficiently specific or clear enough to be actionable. Instead of providing what could have been a very actionable insight (“your right front tire is 18% below the recommended tire pressure and unsafe to drive on”), the tire alert ends up being, in most cases, a useless annoyance.
Similarly, many dashboards share information that isn’t as useful as it could be. Rather than giving us clear insights and direction, they can overwhelm us with too much noise, obscure what’s important (signal), create confusion and raise needless questions. Instead of being empowered with actionable insights, we end up ignoring the data contained within these less effective dashboards. Fortunately, with a little more thought and preparation around the design of your dashboards, you can significantly enhance their actionability by following these 10 guidelines:
1. Target a specific audience.
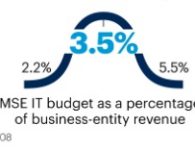
Too often dashboards try to serve too wide an audience. When a broad array of information is included to appease diverse users, the signal-to-noise ratio weakens for everyone. Whether you have users from different functional teams (Marketing vs. Sales) or diverse levels within the same functional group (CMO vs. SEO marketer), the information one set of users finds valuable will often be noise or minutiae for a different set of users. Aside from designing for a specific audience, a dynamic, role-based dashboard can also be used to overcome this challenge, using technology to deliver highly tailored information to diverse individuals based on their unique profile.
If a dashboard tries to serve too wide an audience, the noise-to-insight ratio increases for everyone.
Brent Dykes
2. Involve end users in the design process.
The easiest mistake to make when designing a dashboard is to assume you understand the end users’ insight needs. To be actionable, a dashboard must contain relevant metrics and dimensions that are tied to an audience’s day-to-day responsibilities. Guesswork and assumptions about their information needs will lead disappointment. If a dashboard doesn’t contain the right information or it’s not delivered in the right manner, it won’t be used and won’t drive any action. In my car example, the engineers clearly didn’t understand what information vehicle drivers need to know about tire pressure. If you discuss the users’ requirements upfront and then follow up for feedback, your dashboards are more likely to hit the mark.
3. Provide adequate context.
Without sufficient contextual information, it can be more difficult to know when action is required. By adding background information to key metrics such as period-over-period comparisons, targets, and industry benchmarks, the audience gains a deeper perspective on the displayed results. Urgency to act is introduced when people see they are underperforming compared to a previous time period, expected target or industry average.
Without proper context, the data will not be able to create the needed urgency to act when there’s an issue or gap. Seeing a comparison to another time period or target can lead to meaningful questions and actions.
Brent Dykes
4. Describe how to interpret the numbers.
With differing levels of domain expertise and data literacy across end users, it’s important to explain how the data should be interpreted. If people don’t understand what a metric measures or what it means, your dashboard is less likely to inspire action. Metric definitions and pop-up tooltips can help users to better comprehend the various data elements and charts in your dashboards.
5. Choose the right data charts.
Even though many chart options are available, you’ll often find data tables are overused in dashboards. While data tables can be suitable in some situations (granular comparisons), there are often better, more insightful ways of displaying the numbers. In addition, some charts may be more conducive to yielding meaningful insights than others. For example, it’s often easier to make meaningful comparisons with a bar chart than a pie or donut chart. The more taxing it is to see an insight, the more likely it will be overlooked.
6. Anticipate the flow of questions.
Dashboards should be designed to follow the users’ natural curiosity and logical line of questioning. Having a clear visual hierarchy within the dashboard helps the audience navigate the content. Using an inverted pyramid approach, you begin with high-level KPIs and then lead into breakdowns by relevant dimensions. Rather than encountering frustrating dead ends, a clear content hierarchy and filtering options can guide users to insights that need their attention.
The inverted pyramid approach can be helpful in guiding your dashboard design.
Brent Dykes
7. Streamline for easier consumption.
Displaying too much data can be confusing and overwhelming. Busy, disorganized dashboards can scare away users before they even have a chance to explore the data. As UX expert Steve Krug stated, “If something requires a large investment of time — or looks like it will — it’s less likely to be used.” All forms of clutter should be removed so insights can be easier to see and less taxing to find. At a macro-level, that might mean reducing the number of charts or focusing on familiar chart types. At a micro-level, it may mean removing chartjunk from charts or avoiding excessive granular data.
8. Highlight what’s important.
Most of the information displayed in a dashboard will not be remarkable or noteworthy. In fact, the nondescript data can actually mask unexpected anomalies, trends or patterns that do matter. Either using chart design or technology, potential issues or opportunities can be made visually apparent to users. For example, you could use conditional formatting to highlight underperforming results or provide an acceptable range for a particular metric. (Note: Alerts should be used to complement dashboards by notifying people when key aberrations occur.)
Different visual cues can help the audience to spot key anomalies in the data.
Brent Dykes
9. Recommend prescriptive actions.
Sometimes, an insight may be obvious in the data, but the right course of action isn’t as clear cut. Based on pre-defined business rules, a dashboard can recommend which actions people should take based on a particular insight. If your dashboard doesn’t support automated recommendations, you can provide instructions on what actions to take based on different scenarios such as significant downward or upward swings in key metrics.
10. Review content periodically.
Over time, new content may be added to a dashboard, causing it to become more cluttered. Alternatively, a dashboard may be neglected and become stagnant, causing it to be less and less relevant as time passes. In either situation, a periodic review of your dashboards will ensure they continue to remain focused and aligned to your business priorities. For crucial dashboards, you may want to audit them every six months to ensure they stay aligned and relevant.
Author Napoleon Hill is attributed with saying, “Action is the real measure of intelligence.” Action is also the real measure of business intelligence. Without action, your data will provide little value to your organization. As you apply these tips to the design of your dashboards, you’ll see a shift in their actionability and effectiveness. From business leaders to the frontline employees, actionable dashboards can help inform better decision making at every level. The more actions that can be generated by your dashboards, the greater the impact you’ll see from your overall data investments.
read more at http://www.forbes.com/entrepreneurs/ by Brent Dykes, Contributor
Business